Understanding how businesses are classified by revenue is essential for entrepreneurs, investors, and policymakers. Company revenue scale criteria provide a structured way to categorize organizations based on their annual income. These classifications influence taxation, regulatory requirements, funding eligibility, and competitive positioning. Whether a startup aims to grow into a mid sized enterprise or an established corporation evaluates expansion strategies, revenue benchmarks play a crucial role. By analyzing company revenue scale criteria, stakeholders gain clarity on financial performance standards and market positioning. This framework supports strategic planning, investment decisions, and long term business development in diverse industries.
Defining Company Revenue Scale Criteria
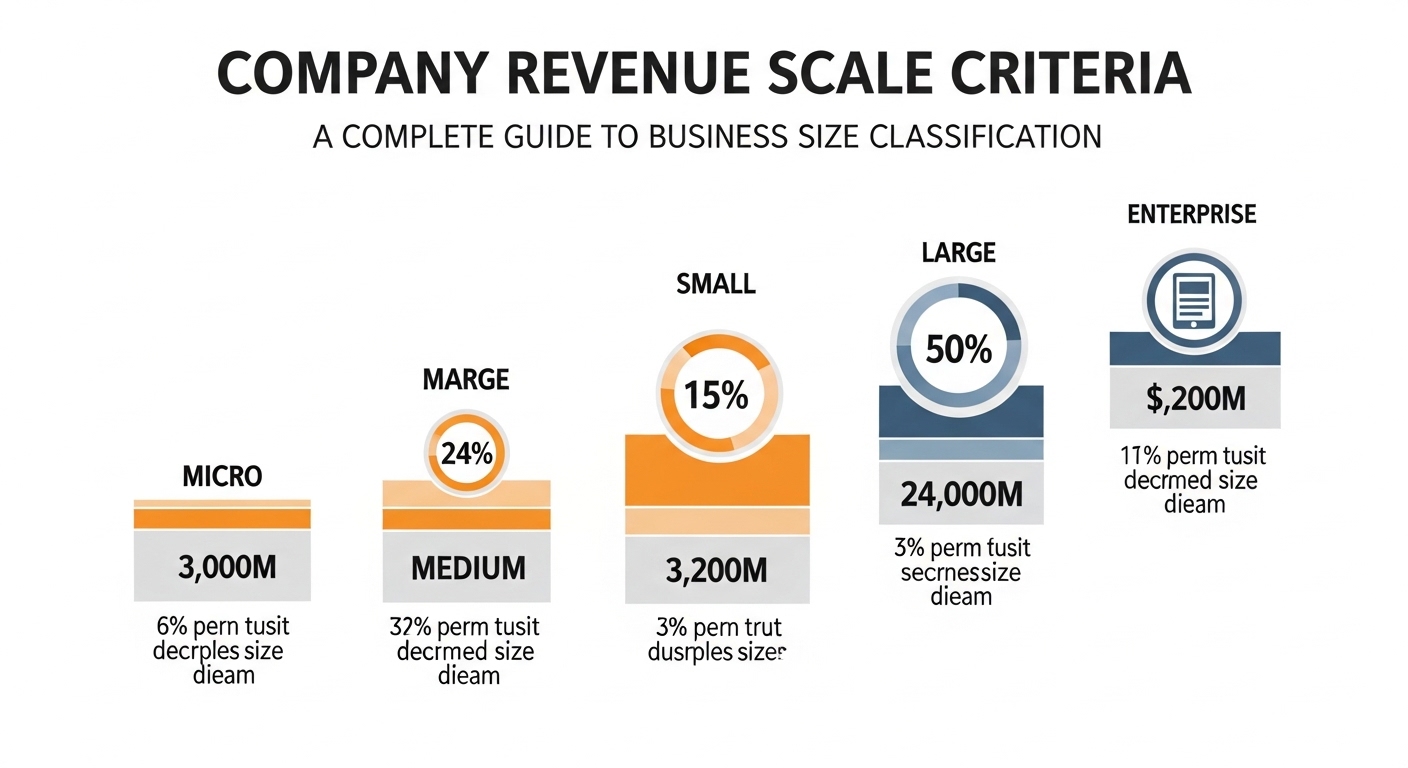
Company revenue scale criteria refer to the financial thresholds used to classify businesses into categories such as small, medium, or large enterprises. These benchmarks typically depend on annual gross revenue, though some frameworks also consider employee count or asset value. Governments and financial institutions rely on these criteria to determine eligibility for support programs and regulatory obligations. Revenue scale definitions vary by country and sector, reflecting economic differences. Understanding these standards helps business owners assess their market status. Clear revenue classifications enable organizations to compare performance against peers and set realistic financial growth targets.
Small Business Revenue Benchmarks
Small businesses form the foundation of many economies and are often defined by modest revenue limits. Company revenue scale criteria typically place small enterprises within a specific annual income range, which can vary by jurisdiction. These thresholds are designed to identify businesses that operate with limited resources and smaller operational capacity. Classification as a small business may provide access to tax benefits, grants, or simplified compliance requirements. Recognizing where a company falls within revenue criteria helps owners align strategies with available support programs. Accurate financial reporting ensures proper classification and avoids regulatory complications.
Medium Sized Enterprise Revenue Standards
Medium sized enterprises occupy a transitional space between small startups and large corporations. Company revenue scale criteria for this category often reflect higher income thresholds and expanded operational complexity. Businesses in this range typically demonstrate stable growth, diversified customer bases, and structured management systems. Being classified as a medium enterprise can influence loan approvals, investor interest, and partnership opportunities. Revenue standards in this category serve as indicators of financial maturity. Understanding these criteria allows business leaders to plan expansion strategies and measure progress toward becoming larger market participants.
Large Corporation Revenue Thresholds
Large corporations exceed upper revenue limits defined within company revenue scale criteria. These organizations often operate across multiple regions or internationally, generating substantial annual income. Higher revenue classification may involve increased regulatory oversight and reporting requirements. Large corporations typically have advanced governance structures and diversified revenue streams. Recognizing the criteria for this category helps executives maintain compliance and manage public accountability. Revenue scale classification also affects competitive analysis, as large companies often influence industry standards and pricing structures. Clear understanding of these thresholds supports strategic planning and corporate governance practices.
Industry Specific Revenue Variations
Company revenue scale criteria are not always uniform across industries. Sectors such as technology, manufacturing, retail, and finance may apply different revenue thresholds based on operational characteristics. For example, capital intensive industries may require higher revenue benchmarks to qualify as medium or large enterprises. Service based businesses might operate efficiently at lower revenue levels. These variations ensure that classification reflects practical realities within each sector. Business owners should consider industry specific standards when evaluating their financial position. Understanding sector based differences enables more accurate benchmarking and strategic decision making.
The Role of Revenue in Investment Decisions
Investors often rely on company revenue scale criteria to assess risk and growth potential. Revenue size can indicate market traction, operational efficiency, and scalability. Early stage investors may focus on startups with lower revenue but high growth rates, while institutional investors often prefer established companies with stable income streams. Classification by revenue scale provides a framework for comparing opportunities. Transparent financial reporting strengthens investor confidence and supports funding negotiations. By understanding revenue criteria, companies can position themselves effectively within competitive capital markets and communicate financial performance clearly.
Regulatory and Tax Implications
Company revenue scale criteria directly influence regulatory compliance and tax obligations. Governments frequently tailor reporting requirements and tax rates according to business size. Smaller enterprises may benefit from simplified accounting procedures, while larger corporations face stricter oversight. Accurate classification ensures compliance with local laws and prevents penalties. Revenue thresholds also determine eligibility for incentives or subsidies designed to encourage economic growth. Business leaders must monitor annual revenue changes to maintain proper classification. Proactive financial management helps organizations adapt to regulatory adjustments and sustain operational stability.
Strategic Planning and Growth Milestones
Revenue scale criteria serve as valuable benchmarks for strategic planning. Companies can set measurable goals aligned with desired classification levels. Transitioning from small to medium enterprise status may signal successful expansion, while reaching large corporation thresholds reflects sustained growth. Clear milestones encourage disciplined financial management and performance tracking. Understanding company revenue scale criteria allows leaders to anticipate operational adjustments required at each stage. Growth planning based on defined revenue benchmarks supports resource allocation, workforce expansion, and market development strategies that align with long term objectives.
Global Perspectives on Revenue Classification
Different countries apply unique company revenue scale criteria based on economic conditions and policy objectives. International businesses must understand varying thresholds when operating across borders. Revenue classifications may influence trade agreements, cross border taxation, and compliance obligations. Multinational enterprises often navigate multiple regulatory frameworks simultaneously. Awareness of global revenue standards ensures consistent reporting and strategic alignment. By studying international benchmarks, companies can adapt their expansion plans to diverse markets. Understanding these global perspectives enhances competitiveness and supports informed decision making in international business environments.
Conclusion
Company revenue scale criteria provide a structured framework for categorizing businesses by financial performance. These classifications influence taxation, regulatory requirements, investment decisions, and strategic planning. From small enterprises to large corporations, revenue benchmarks guide organizational growth and compliance responsibilities. Industry variations and global differences further shape how businesses interpret and apply these standards. By understanding company revenue scale criteria, leaders can make informed decisions, set realistic milestones, and strengthen financial transparency. Clear revenue classification ultimately supports sustainable development and competitive positioning in an evolving global economy.